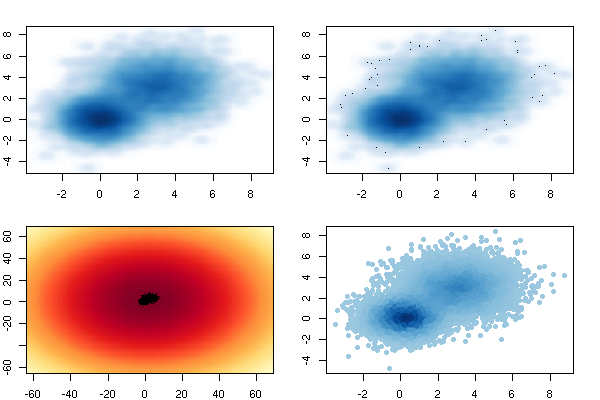
Additional features in R over other analytical packages-
1) Source Code is given to ensure complete custom solution and embedding for a particular application. Open source code has an advantage that is extensively peer- reviewed in Journals and Scientific Literature. This means bugs will found, shared and corrected transparently.
2) Wide literature of training material in the form of books is available for the R analytical platform.
3) Extensively the best data visualization tools in analytical software (apart from Tableau Software ‘s latest version). The extensive data visualization available in R is of the form a variety of customizable graphs, as well as animation. The principal reason third-party software initially started creating interfaces to R is because the graphical library of packages in R is more advanced as well as rapidly getting more features by the day.
4) Free in upfront license cost for academics and thus budget friendly for small and large analytical teams.
5) Flexible programming for your data environment. This includes having packages that ensure compatibility with Java, Python and C++.
6) Easy migration from other analytical platforms to R Platform. It is relatively easy for a non R platform user to migrate to R platform and there is no danger of vendor lock-in due to the GPL nature of source code and open community.
Statistics are numbers that tell (descriptive), advise ( prescriptive) or forecast (predictive). Analytics is a decision-making help tool. Analytics on which no decision is to be made or is being considered can be classified as purely statistical and non analytical. Thus ease of making a correct decision separates a good analytical platform from a not so good analytical platform. The distinction is likely to be disputed by people of either background- and business analysis requires more emphasis on how practical or actionable the results are and less emphasis on the statistical metrics in a particular data analysis task. I believe one clear reason between business analytics is different from statistical analysis is the cost of perfect information (data costs in real world) and the opportunity cost of delayed and distorted decision-making.
Specific to the following domains R has the following costs and benefits
- Business Analytics
- R is free per license and for download
- It is one of the few analytical platforms that work on Mac OS
- It’s results are credibly established in both journals like Journal of Statistical Software and in the work at LinkedIn, Google and Facebook’s analytical teams.
- It has open source code for customization as per GPL
- It also has a flexible option for commercial vendors like Revolution Analytics (who support 64 bit windows) as well as bigger datasets
- It has interfaces from almost all other analytical software including SAS,SPSS, JMP, Oracle Data Mining, Rapid Miner. Existing license holders can thus invoke and use R from within these software
- Huge library of packages for regression, time series, finance and modeling
- High quality data visualization packages
- Data Mining
- R as a computing platform is better suited to the needs of data mining as it has a vast array of packages covering standard regression, decision trees, association rules, cluster analysis, machine learning, neural networks as well as exotic specialized algorithms like those based on chaos models.
- Flexibility in tweaking a standard algorithm by seeing the source code
- The RATTLE GUI remains the standard GUI for Data Miners using R. It was created and developed in Australia.
- Business Dashboards and Reporting
- Business Dashboards and Reporting are an essential piece of Business Intelligence and Decision making systems in organizations. R offers data visualization through GGPLOT, and GUI like Deducer and Red-R can help even non R users create a metrics dashboard
- For online Dashboards- R has packages like RWeb, RServe and R Apache- which in combination with data visualization packages offer powerful dashboard capabilities.
- R can be combined with MS Excel using the R Excel package – to enable R capabilities to be imported within Excel. Thus a MS Excel user with no knowledge of R can use the GUI within the R Excel plug-in to use powerful graphical and statistical capabilities.
Additional factors to consider in your R installation-
There are some more choices awaiting you now-
1) Licensing Choices-Academic Version or Free Version or Enterprise Version of R
2) Operating System Choices-Which Operating System to choose from? Unix, Windows or Mac OS.
3) Operating system sub choice- 32- bit or 64 bit.
4) Hardware choices-Cost -benefit trade-offs for additional hardware for R. Choices between local ,cluster and cloud computing.
5) Interface choices-Command Line versus GUI? Which GUI to choose as the default start-up option?
6) Software component choice- Which packages to install? There are almost 3000 packages, some of them are complimentary, some are dependent on each other, and almost all are free.
7) Additional Software choices- Which additional software do you need to achieve maximum accuracy, robustness and speed of computing- and how to use existing legacy software and hardware for best complementary results with R.
1) Licensing Choices-
You can choose between two kinds of R installations – one is free and open source from http://r-project.org The other R installation is commercial and is offered by many vendors including Revolution Analytics. However there are other commercial vendors too.
Commercial Vendors of R Language Products-
1) Revolution Analytics http://www.revolutionanalytics.com/
2) XL Solutions- http://www.experience-rplus.com/
3) Information Builder – Webfocus RStat -Rattle GUI http://www.informationbuilders.com/products/webfocus/PredictiveModeling.html
4) Blue Reference- Inference for R http://inferenceforr.com/default.aspx
- Choosing Operating System
-
- Windows
-
Windows remains the most widely used operating system on this planet. If you are experienced in Windows based computing and are active on analytical projects- it would not make sense for you to move to other operating systems. This is also based on the fact that compatibility problems are minimum for Microsoft Windows and the help is extensively documented. However there may be some R packages that would not function well under Windows- if that happens a multiple operating system is your next option.
-
-
-
- Enterprise R from Revolution Analytics- Enterprise R from Revolution Analytics has a complete R Development environment for Windows including the use of code snippets to make programming faster. Revolution is also expected to make a GUI available by 2011. Revolution Analytics claims several enhancements for it’s version of R including the use of optimized libraries for faster performance.
- MacOS
-
-
Reasons for choosing MacOS remains its considerable appeal in aesthetically designed software- but MacOS is not a standard Operating system for enterprise systems as well as statistical computing. However open source R claims to be quite optimized and it can be used for existing Mac users. However there seem to be no commercially available versions of R available as of now for this operating system.
-
-
- Linux
-
-
-
-
- Ubuntu
- Red Hat Enterprise Linux
- Other versions of Linux
-
-
Linux is considered a preferred operating system by R users due to it having the same open source credentials-much better fit for all R packages and it’s customizability for big data analytics.
Ubuntu Linux is recommended for people making the transition to Linux for the first time. Ubuntu Linux had an marketing agreement with revolution Analytics for an earlier version of Ubuntu- and many R packages can installed in a straightforward way as Ubuntu/Debian packages are available. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is officially supported by Revolution Analytics for it’s enterprise module. Other versions of Linux popular are Open SUSE.
-
-
- Multiple operating systems-
- Virtualization vs Dual Boot-
- Multiple operating systems-
-
You can also choose between having a VMware VM Player for a virtual partition on your computers that is dedicated to R based computing or having operating system choice at the startup or booting of your computer. A software program called wubi helps with the dual installation of Linux and Windows.
- 64 bit vs 32 bit – Given a choice between 32 bit versus 64 bit versions of the same operating system like Linux Ubuntu, the 64 bit version would speed up processing by an approximate factor of 2. However you need to check whether your current hardware can support 64 bit operating systems and if so- you may want to ask your Information Technology manager to upgrade atleast some operating systems in your analytics work environment to 64 bit operating systems.
- Hardware choices- At the time of writing this book, the dominant computing paradigm is workstation computing followed by server-client computing. However with the introduction of cloud computing, netbooks, tablet PCs, hardware choices are much more flexible in 2011 than just a couple of years back.
Hardware costs are a significant cost to an analytics environment and are also remarkably depreciated over a short period of time. You may thus examine your legacy hardware, and your future analytical computing needs- and accordingly decide between the various hardware options available for R.
Unlike other analytical software which can charge by number of processors, or server pricing being higher than workstation pricing and grid computing pricing extremely high if available- R is well suited for all kinds of hardware environment with flexible costs. Given the fact that R is memory intensive (it limits the size of data analyzed to the RAM size of the machine unless special formats and /or chunking is used)- it depends on size of datasets used and number of concurrent users analyzing the dataset. Thus the defining issue is not R but size of the data being analyzed.
-
- Local Computing- This is meant to denote when the software is installed locally. For big data the data to be analyzed would be stored in the form of databases.
- Server version- Revolution Analytics has differential pricing for server -client versions but for the open source version it is free and the same for Server or Workstation versions.
- Workstation
- Cloud Computing- Cloud computing is defined as the delivery of data, processing, systems via remote computers. It is similar to server-client computing but the remote server (also called cloud) has flexible computing in terms of number of processors, memory, and data storage. Cloud computing in the form of public cloud enables people to do analytical tasks on massive datasets without investing in permanent hardware or software as most public clouds are priced on pay per usage. The biggest cloud computing provider is Amazon and many other vendors provide services on top of it. Google is also coming for data storage in the form of clouds (Google Storage), as well as using machine learning in the form of API (Google Prediction API)
- Amazon
- Cluster-Grid Computing/Parallel processing- In order to build a cluster, you would need the RMpi and the SNOW packages, among other packages that help with parallel processing.
- How much resources
- RAM-Hard Disk-Processors- for workstation computing
- Instances or API calls for cloud computing
- Local Computing- This is meant to denote when the software is installed locally. For big data the data to be analyzed would be stored in the form of databases.
- Interface Choices
- Command Line
- GUI
- Web Interfaces
- Software Component Choices
- R dependencies
- Packages to install
- Recommended Packages
- Additional software choices
- Additional legacy software
- Optimizing your R based computing
- Code Editors
- Code Analyzers
- Libraries to speed up R
citation- R Development Core Team (2010). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing,Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org.
(Note- this is a draft in progress)
Related Articles
- Are You a Computer Science Student? Want To Be a Data Scientist? Then Check This Out (readwriteweb.com)
- Why Use R? (r-bloggers.com)