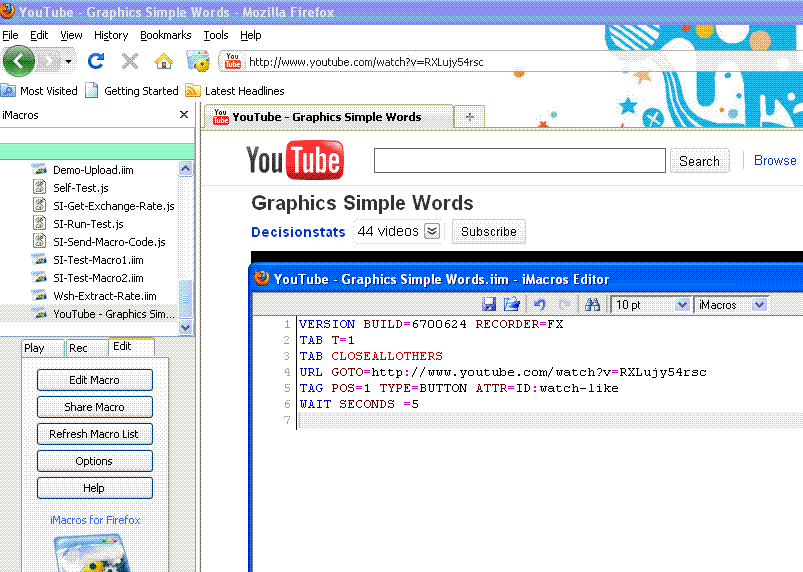
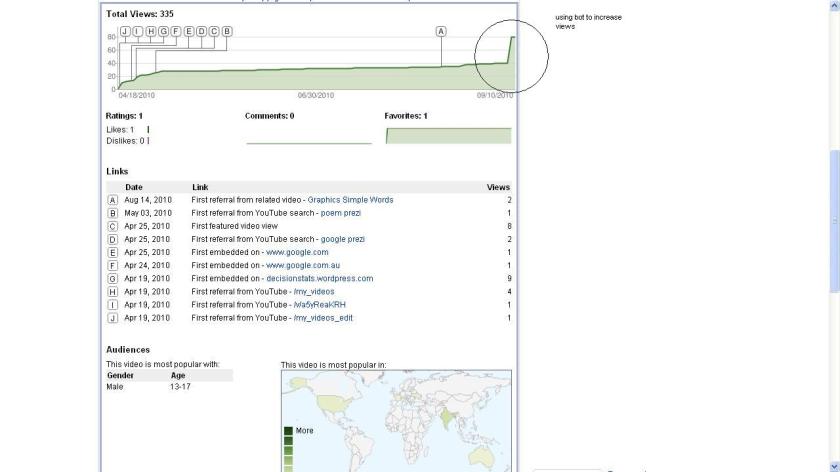
Just checked out cool new series from NVidia servers.
Now though SAS Inc/ Jim Goodnight thinks HP Blade Servers are the cool thing- the GPU takes hardware high performance computing to another level. It would be interesting to see GPU based cloud computers as well – say for the on Demand SAS (free for academics and students) but which has had some complaints of being slow.
See this for SAS and Blade Servers-
http://www.sas.com/success/ncsu_analytics.html
To give users hands-on experience, the program is underpinned by a virtual computing lab (VCL), a remote access service that allows users to reserve a computer configured with a desired set of applications and operating system and then access that computer over the Internet. The lab is powered by an IBM BladeCenter infrastructure, which includes more than 500 blade servers, distributed between two locations. The assignment of the blade servers can be changed to meet shifts in the balance of demand among the various groups of users. Laura Ladrie, MSA Classroom Coordinator and Technical Support Specialist, says, “The virtual computing lab chose IBM hardware because of its quality, reliability and performance. IBM hardware is also energy efficient and lends itself well to high performance/low overhead computing.
Thats interesting since IBM now competes (as owner of SPSS) and also cooperates with SAS Institute
And
http://www.theaustralian.com.au/australian-it/the-world-according-to-jim-goodnight-blade-switch-slashes-job-times/story-e6frgakx-1225888236107

You’re effectively turbo-charging through deployment of many processors within the blade servers?
Yes. We’ve got machines with 192 blades on them. One of them has 202 or 203 blades. We’re using Hewlett-Packard blades with 12 CP cores on each, so it’s a total 2300 CPU cores doing the computation.
Our idea was to give every one of those cores a little piece of work to do, and we came up with a solution. It involved a very small change to the algorithm we were using, and it’s just incredible how fast we can do things now.
I don’t think of it as a grid, I think of it as essentially one computer. Most people will take a blade and make a grid out of it, where everything’s a separate computer running separate jobs.
We just look at it as one big machine that has memory and processors all over the place, so it’s a totally different concept.
GPU servers can be faster than CPU servers, though , Professor G.
Source-
http://www.nvidia.com/object/preconfigured_clusters.html
TESLA GPU COMPUTING SOLUTIONS FOR DATA CENTERS
Supercharge your cluster with the Tesla family of GPU computing solutions. Deploy 1U systems from NVIDIA or hybrid CPU-GPU servers from OEMs that integrate NVIDIA® Tesla™ GPU computing processors.
When compared to the latest quad-core CPU, Tesla 20-series GPU computing processors deliver equivalent performance at 1/20th the power consumption and 1/10th the cost. Each Tesla GPU features hundreds of parallel CUDA cores and is based on the revolutionary NVIDIA® CUDA™ parallel computing architecture with a rich set of developer tools (compilers, profilers, debuggers) for popular programming languages APIs like C, C++, Fortran, and driver APIs like OpenCL and DirectCompute.
NVIDIA’s partners provide turnkey easy-to-deploy Preconfigured Tesla GPU clusters that are customizable to your needs. For 3D cloud computing applications, our partners offer the Tesla RS clusters that are optimized for running RealityServer with iray.
Available Tesla Products for Data Centers:
– Tesla S2050
– Tesla M2050/M2070
– Tesla S1070
– Tesla M1060
Also I liked the hybrid GPU and CPU

And from a paper on comparing GPU and CPU using Benchmark tests on BLAS from a Debian- Dirk E’s excellent blog
http://dirk.eddelbuettel.com/blog/
Usage of accelerated BLAS libraries seems to shrouded in some mystery, judging from somewhat regularly recurring requests for help on lists such as r-sig-hpc(gmane version), the R list dedicated to High-Performance Computing. Yet it doesn’t have to be; installation can be really simple (on appropriate systems).
Another issue that I felt needed addressing was a comparison between the different alternatives available, quite possibly including GPU computing. So a few weeks ago I sat down and wrote a small package to run, collect, analyse and visualize some benchmarks. That package, called gcbd (more about the name below) is now onCRAN as of this morning. The package both facilitates the data collection for the paper it also contains (in the vignette form common among R packages) and provides code to analyse the data—which is also included as a SQLite database. All this is done in the Debian and Ubuntu context by transparently installing and removing suitable packages providing BLAS implementations: that we can fully automate data collection over several competing implementations via a single script (which is also included). Contributions of benchmark results is encouraged—that is the idea of the package.
And from his paper on the same-
Analysts are often eager to reap the maximum performance from their computing platforms.
A popular suggestion in recent years has been to consider optimised basic linear algebra subprograms (BLAS). Optimised BLAS libraries have been included with some (commercial) analysis platforms for a decade (Moler 2000), and have also been available for (at least some) Linux distributions for an equally long time (Maguire 1999). Setting BLAS up can be daunting: the R language and environment devotes a detailed discussion to the topic in its Installation and Administration manual (R Development Core Team 2010b, appendix A.3.1). Among the available BLAS implementations, several popular choices have emerged. Atlas (an acronym for Automatically Tuned Linear Algebra System) is popular as it has shown very good performance due to its automated and CPU-speci�c tuning (Whaley and Dongarra 1999; Whaley and Petitet 2005). It is also licensed in such a way that it permits redistribution leading to fairly wide availability of Atlas.1 We deploy Atlas in both a single-threaded and a multi-threaded con�guration. Another popular BLAS implementation is Goto BLAS which is named after its main developer, Kazushige Goto (Goto and Van De Geijn 2008). While `free to use’, its license does not permit redistribution putting the onus of con�guration, compilation and installation on the end-user. Lastly, the Intel Math Kernel Library (MKL), a commercial product, also includes an optimised BLAS library. A recent addition to the tool chain of high-performance computing are graphical processing units (GPUs). Originally designed for optimised single-precision arithmetic to accelerate computing as performed by graphics cards, these devices are increasingly used in numerical analysis. Earlier criticism of insu�cient floating-point precision or severe performance penalties for double-precision calculation are being addressed by the newest models. Dependence on particular vendors remains a concern with NVidia’s CUDA toolkit (NVidia 2010) currently still the preferred development choice whereas the newer OpenCL standard (Khronos Group 2008) may become a more generic alternative that is independent of hardware vendors. Brodtkorb et al. (2010) provide an excellent recent survey. But what has been lacking is a comparison of the e�ective performance of these alternatives. This paper works towards answering this question. By analysing performance across �ve di�erent BLAS implementations|as well as a GPU-based solution|we are able to provide a reasonably broad comparison.
Performance is measured as an end-user would experience it: we record computing times from launching commands in the interactive R environment (R Development Core Team 2010a) to their completion.
And
Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) provide an Application Programming Interface
(API) for linear algebra. For a given task such as, say, a multiplication of two conformant
matrices, an interface is described via a function declaration, in this case sgemm for single
precision and dgemm for double precision. The actual implementation becomes interchangeable
thanks to the API de�nition and can be supplied by di�erent approaches or algorithms. This
is one of the fundamental code design features we are using here to benchmark the di�erence
in performance from di�erent implementations.
A second key aspect is the di�erence between static and shared linking. In static linking,
object code is taken from the underlying library and copied into the resulting executable.
This has several key implications. First, the executable becomes larger due to the copy of
the binary code. Second, it makes it marginally faster as the library code is present and
no additional look-up and subsequent redirection has to be performed. The actual amount
of this performance penalty is the subject of near-endless debate. We should also note that
this usually amounts to only a small load-time penalty combined with a function pointer
redirection|the actual computation e�ort is unchanged as the actual object code is identi-
cal. Third, it makes the program more robust as fewer external dependencies are required.
However, this last point also has a downside: no changes in the underlying library will be
reected in the binary unless a new build is executed. Shared library builds, on the other
hand, result in smaller binaries that may run marginally slower|but which can make use of
di�erent libraries without a rebuild.
Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms (BLAS) provide an Application Programming Interface(API) for linear algebra. For a given task such as, say, a multiplication of two conformantmatrices, an interface is described via a function declaration, in this case sgemm for singleprecision and dgemm for double precision. The actual implementation becomes interchangeablethanks to the API de�nition and can be supplied by di�erent approaches or algorithms. Thisis one of the fundamental code design features we are using here to benchmark the di�erencein performance from di�erent implementations.A second key aspect is the di�erence between static and shared linking. In static linking,object code is taken from the underlying library and copied into the resulting executable.This has several key implications. First, the executable becomes larger due to the copy ofthe binary code. Second, it makes it marginally faster as the library code is present andno additional look-up and subsequent redirection has to be performed. The actual amountof this performance penalty is the subject of near-endless debate. We should also note thatthis usually amounts to only a small load-time penalty combined with a function pointerredirection|the actual computation e�ort is unchanged as the actual object code is identi-cal. Third, it makes the program more robust as fewer external dependencies are required.However, this last point also has a downside: no changes in the underlying library will bereected in the binary unless a new build is executed. Shared library builds, on the otherhand, result in smaller binaries that may run marginally slower|but which can make use ofdi�erent libraries without a rebuild.
And summing up,
reference BLAS to be dominated in all cases. Single-threaded Atlas BLAS improves on the reference BLAS but loses to multi-threaded BLAS. For multi-threaded BLAS we �nd the Goto BLAS dominate the Intel MKL, with a single exception of the QR decomposition on the xeon-based system which may reveal an error. The development version of Atlas, when compiled in multi-threaded mode is competitive with both Goto BLAS and the MKL. GPU computing is found to be compelling only for very large matrix sizes. Our benchmarking framework in the gcbd package can be employed by others through the R packaging system which could lead to a wider set of benchmark results. These results could be helpful for next-generation systems which may need to make heuristic choices about when to compute on the CPU and when to compute on the GPU.
Source – DirkE’paper and blog http://dirk.eddelbuettel.com/papers/gcbd.pdf
Quite appropriately-,
Hardware solutions or atleast need to be a part of Revolution Analytic’s thinking as well. SPSS does not have any choice anymore though 😉
It would be interesting to see how the new SAS Cloud Computing/ Server Farm/ Time Sharing facility is benchmarking CPU and GPU for SAS analytics performance – if being done already it would be nice to see a SUGI paper on the same at http://sascommunity.org.
Multi threading needs to be taken care automatically by statistical software to optimize current local computing (including for New R)
Acceptable benchmarks for testing hardware as well as software need to be reinforced and published across vendors, academics and companies.
What do you think?
35.965000
-83.920000






 Journal
Journal