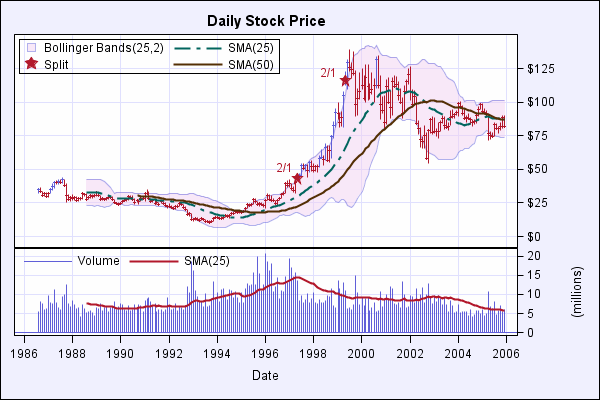
Here is an interview with Prof John Fox, creator of the very popular R language based GUI, RCmdr.

Ajay- Describe your career in science from your high school days to the science books you have written. What do you think can be done to increase interest in science in young people.
John Fox- I’m a sociologist and social statistician, so I don’t have a career in science, as that term is generally understood. I was interested in science as a child, however: I attended a science high school in New York City (Brooklyn Tech), and when I began university in 1964 at New York’s City College, I started in engineering. I moved subsequently through majors in philosophy and psychology, before finishing in sociology — had I not graduated in 1968 I probably would have moved on to something else. I took a statistics course during my last year as an undergraduate and found it fascinating. I enrolled in the sociology graduate program at the University of Michigan, where I specialized in social psychology and demography, and finished with a PhD in 1972 when I was 24 years old. I became interested in computers during my first year in graduate school, where I initially learned to program in Fortran. I also took quite a few courses in statistics and math.
I haven’t written any science books, but I have written and edited a number of books on social statistics, including, most recently, Applied Regression Analysis and Generalized Linear Models, Second Edition (Sage, 2008).
I’m afraid that I don’t know how to interest young people in science. Science seemed intrinsically interesting to me when I was young, and still does.
Ajay- What prompted you to R Commander. How would you describe R Commander as a tool, say for a user of other languages and who want to learn R, but get afraid of the syntax.
John- I originally programmed the R Commander so that I could use R to teach introductory statistics courses to sociology undergraduates. I previously taught this course with Minitab or SPSS, which were programs that I never used for my own work. I waited for someone to come up with a simple, portable, easily installed point-and-click interface to R, but nothing appeared on the horizon, and so I decided to give it a try myself.
I suppose that the R Commander can ease users into writing commands, inasmuch as the commands are displayed, but I suspect that most users don’t look at them. I think that serious prospective users of R should be encouraged to use the command-line interface along with a script editor of some sort. I wouldn’t exaggerate the difficulty of learning R: I came to R — actually S then — after having programmed in perhaps a dozen other languages, most recently at that point Lisp, and found the S language particularly easy to pick up.
Ajay- I particularly like the R Cmdr plugins. Is it possible for anyone to increase R Commander with a customized package- plugin.
John- That’s the basic idea, though the plug-in author has to be able to program in R and must learn a little Tcl/Tk.
Ajay- Have you thought of using the R Commander GUI on an Amazon EC2 and thus making R high performance computing say available on demand ( similar to Zementis model deployment using Amazon Ec2). What are you views on the future of statistical computing
John- I’m not sure whether or how an interface like the Rcmdr, which is Tcl/Tk-based, can be adapted to cloud computing. I also don’t feel qualified to predict the future of statistical computing.
I think that R is where the action is for the near future.
Ajay-What are the best ways for using R Commander as a teaching tool ( I noticed the help is a bit outdated).
John- Is the help a bit outdated? My intention is that the R Commander should be largely self-explanatory. Most people know how to use point-and-click interfaces. In the basic courses for which it is principally designed, my goals are to teach the essential ideas of statistical reasoning and some skills in data analysis. In this kind of course, statistical software should facilitate the basic goals of the course.
As I said, for serious data analysis, I believe that it’s a good idea to encourage use of the command-line interface.
Ajay- What are your views on R being recognized by SAS Institute for it’s IML product. Do you think there can be a middle way for open source and proprietary software to exist.
John- I imagine that R is a challenge for producers of proprietary software like SAS, partly because R development moves more quickly, but also because R is giving away something that SAS and other vendors of proprietary statistical software are selling. For example, I once used SAS quite a bit but don’t anymore. I also have the sense that for some time SAS has directed its energies more toward business uses of its software than toward purely statistical applications.
Ajay- Do people in R Core team recognize the importance of GUI? What does the rest of R community feel? What has the feedback of users ben to you. Any plans to corporate sponsors for R Commander ( Rattle , an R language data mining GUI has a version called Rstat at http://www.informationbuilders.com/products/webfocus/predictivemodeling.html while the free version and code is at rattle.togaware.com)
John- I feel that the R Commander GUI has been generally positively received, both by members of R Core who have said something about it to me and by others in the R community. Of course, a nice feature of the R package system is that people can simply ignore packages in which they have no interest. I noticed recently that a Journal of Statistical Software paper that I wrote several years ago on the Rcmdr package has been downloaded nearly 35,000 times.
Because I wouldn’t expect many students using the Rcmdr package in a course to read that paper, I expect that the package is being used fairly widely.
Ajay- What does John Fox do for fun or as a hobby?
John- I’m tempted to say that much of my work is fun — particularly doing research, writing programs, and writing papers and books. I used to be quite a serious photographer, but I haven’t done that in years, and the technology of photography has changed a great deal. I run and swim for exercise, but that’s not really fun. I like to read and to travel, but who doesn’t?
Biography-
Prof John Fox is a giant in his chosen fields and has edited/authored 13 books and written chapters for 12 more books. He has also written and been published in almost 49 Journal articles. He is also editor in chief for R News newsletter. You can read more about Dr Fox at http://socserv.mcmaster.ca/jfox/
On R Cmdr-
R Cmdr has substantially decreased the hygiene factor for people wanting to learn R- they begin with the GUI and then later transition to customization using command line. It is so simple in its design that even under graduates have started basic data analysis with R Cmdr after just a class.You can read more on it here at http://socserv.mcmaster.ca/jfox/Misc/Rcmdr/Getting-Started-with-the-Rcmdr.pdf