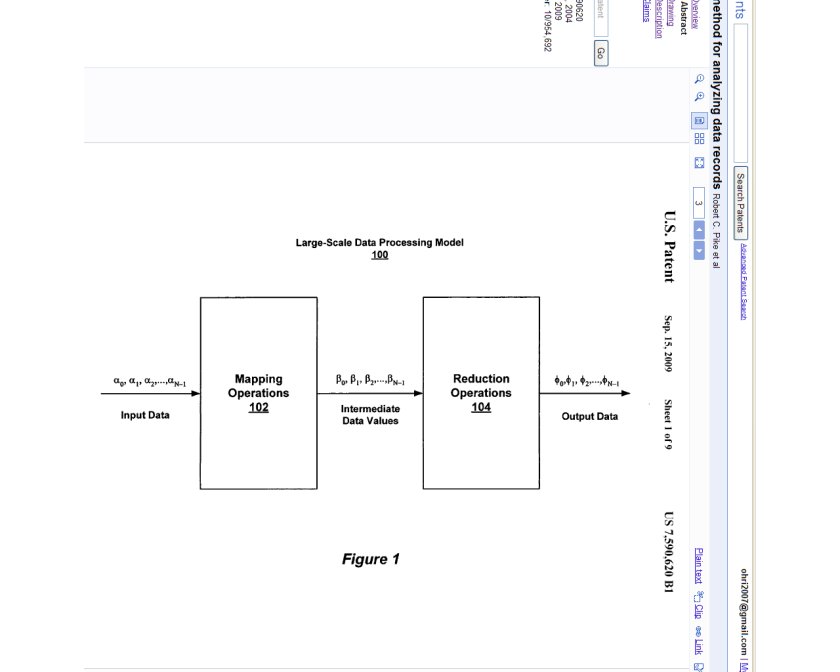
What is claimed is:1. A computer-implemented method of analyzing data records, comprising:
- storing the data records in one or more data centers;
- allocating groups of the stored data records to respective processes of a first plurality of processes executing in parallel;
- after allocating the groups of the stored data records to the respective processes of the first plurality of processes executing in parallel, in each respective process of the first plurality of processes:
-
- for each data record in at least a subset of the group of the stored data records allocated to the respective process:
- creating a parsed representation of the data record;
- applying a procedural language query to the parsed representation of the data record to extract one or more values, wherein the procedural language query is applied independently to each parsed representation; and
- applying a respective emit operator to at least one of the extracted one or more values to add corresponding information to a respective intermediate data structure, wherein the respective emit operator implements one of a predefined set of application-independent statistical information processing functions;
- in each process of a second plurality of processes, aggregating information from a subset of the intermediate data structures to produce aggregated data; and
- combining the produced aggregated data to produce output data.
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the respective emit operator implements one of a predefined set of application-independent statistical information processing functions.
3. The method of claim 2, wherein the application-independent statistical information processing functions comprise one or more of the following: a function for counting occurrences of distinct values, a maximum value function, a minimum value function, a statistical sampling function, a function for identifying values that occur most frequently, and a function for estimating a total number of unique values.
4. The method of claim 1, wherein the applying the procedural language query to the parsed representation of the data record to extract the one or more values and the applying the respective emit operator to at least one of the one or more values to add the corresponding information to the respective intermediate data structure are performed independently for each data record.
5. The method of claim 1, wherein the parsed representation of the data record comprises a key-value pair.
6. The method of claim 1, wherein the intermediate data structure comprises a table having at least one index whose index values comprise unique values of the extracted one or more values.
7. The method of claim 6, wherein the aggregating information from the subset of the intermediate data structures to produce the aggregated data combines the extracted one or more values having the same index values.
8. The method of claim 1, wherein
- when applying the procedural language query to the parsed representation produces a plurality of values, applying the respective emit operator to each of the produced plurality of values to add corresponding information to the respective intermediate data structure.
9. The method of claim 1, wherein the second plurality of processes are executing in parallel.
10. The method of claim 1, wherein the allocating the groups of the stored data records to the respective processes of the first plurality of processes executing in Parallel is application independent, and the procedural language query is application dependent.
11. The method of claim 1, wherein the data records comprise one or more of the following types of data records: log files, transaction records, and documents.
12. The method of claim 1, wherein the intermediate data structure is a table having a plurality of indices, wherein each of the plurality of indices is dynamically generated in accordance with the extracted one or more values.
13. A computer-implemented method of analyzing data records, comprising:
- storing the data records in one or more data centers;
- allocating groups of the stored data records to respective processes of a first plurality of processes executing in parallel;
- after allocating the groups of the stored data records to the respective processes of the first plurality of processes executing in parallel, in each respective process of the first plurality of processes:
-
- for each data record in at least a subset of the group of stored data records allocated to the respective process:
- creating a parsed representation of the data record;
- applying a procedural language query to the parsed representation of the data record to extract one or more values; and
- applying a respective operator to at least one of the extracted one or more values to add corresponding information to a respective intermediate data structure;
- in each process of a second plurality of processes, aggregating information from a subset of the intermediate data structures to produce aggregated data; and
- combining the produced aggregated data to produce output data.
14. A computer system with one or more processors and memory for analyzing data records, wherein the data records are stored in one or more data centers, the computer system comprising:
- a first plurality of processes operating in parallel, each of which is allocated a group of stored data records to process;
- each respective process of the first plurality of processes including instructions for:
-
- creating a parsed representation of each data record in at least a subset of the group of stored data records allocated to the respective process after the group of stored data records is allocated to the respective process;
-
- applying a procedural language query to the parsed representation of each stored data record in at least the subset of the group of stored data records allocated to the respective process to produce one or more values; and
- applying one or more emit operators to each of the one or more produced values to add corresponding information to an intermediate data structure; and
- at least one aggregating process for aggregating information from a plurality of the intermediate data structures to produce output data.
15. The system of claim 14, wherein the at least one aggregating process for aggregating information comprises a second plurality of processes operating in parallel, wherein each respective process of the second plurality of processes operating in parallel includes instructions for aggregating information from the plurality of the intermediate data structures to produce the output data.
16. The system of claim 14, wherein the intermediate data structure comprises a table.
17. The system of claim 15, wherein at least one process of the second plurality of processes operating in parallel includes instructions for combining the output data to produce aggregated output data.
18. The system of claim 14, wherein each of the one or more emit operators implements one of a predefined set of application-independent statistical information processing functions.
19. The system of claim 18, wherein the application-independent statistical information processing functions comprise one or more of the following: a function for counting occurrences of distinct values, a maximum value function, a minimum value function, a statistical sampling function, a function for identifying values that occur most frequently, and a function for estimating a total number of unique values.
20. The system of claim 14, wherein the instructions for applying the procedural language query to the parsed representation of each data record in at least the subset of the group of stored data records allocated to the respective process to produce the one or more values include instructions for applying the procedural language query independently to each data record.
21. The system of claim 14, wherein the instructions for applying the procedural language query to the parsed representation of each data record in at least the subset of the group of stored data records allocated to the respective process to produce the one or more values and instructions for applying the one or more emit operators to each of the one or more produced values to add the corresponding information to the intermediate data structure include instructions for applying the procedural language query and the one or more emit operators independently to each data record.
22. The system of claim 14, wherein the at least one aggregating process for aggregating information is configured to aggregate, in each respective process of a second plurality of processes, the information from the plurality of the intermediate data structures to produce the output data.
23. The system of claim 14, wherein each parsed representation of each data record comprises a key-value pair.
24. The system of claim 14, wherein the intermediate data structure comprises a table having at least one index whose index values comprise unique values of the produced values.
25. The system of claim 24, wherein the at least one aggregating process for aggregating the information from the plurality of intermediate data structures to produce the output data includes instructions for combining the one or more produced values having the same index values.
26. The system of claim 14, wherein the instructions for applying the procedural language query to the parsed representation of each stored data record include instructions for applying the one or more emit operators to each of a plurality of produced values to add corresponding information to the intermediate data structure.
27. The system of claim 14, wherein the at least one aggregating process for aggregating the information from the plurality of intermediate data structures to produce the output data comprises a second plurality of processes executing in parallel.
28. The system of claim 14, wherein the system is configured such that the allocation of stored data records to each respective process of the first plurality of processes is application independent, and wherein the procedural language query is application dependent.
29. The system of claim 14, wherein the data records comprise one or more of the following types of data records: log files, transaction records, and documents.
30. The system of claim 14, wherein the intermediate data structure is a table having a plurality of indices, wherein each of the plurality of the indices is dynamically generated in accordance with the one or more produced values.