What were The Opium Wars?
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Opium_Wars
The Opium Wars, also known as the Anglo-Chinese Wars, divided into the First Opium War from 1839 to 1842 and the Second Opium War from 1856 to 1860. These were the climax of disputes over trade and diplomatic relations between China under the Qing Dynasty and the British Empire.
The import of opium into China stood at 200 chests (annual) in 1729,[1] when the first anti-opium edict was promulgated.[2][3] This edict was weakly enforced,[3] and by the time Chinese authorities reissued the prohibition in starker terms in 1799,[4] the figure had leaped; 4,500 chests were imported in the year 1800.[1] The decade of the 1830s witnessed a rapid rise in opium trade,[5] and by 1838 (just before the first Opium War) it climbed to 40,000 chests.[1][5]
Considering that importation of opium into China had been virtually banned by Chinese law, the East India Company established an elaborate trading scheme partially relying on legal markets, and partially leveraging illicit ones. British merchants carrying no opium would buy tea in Canton on credit, and would balance their debts by selling opium at auction in Calcutta. From there, the opium would reach the Chinese coast hidden aboard British ships then smuggled into China by native merchants. In 1797 the company further tightened its grip on the opium trade by enforcing direct trade between opium farmers and the British, and ending the role of Bengali purchasing agents. British exports of opium to China grew from an estimated 15 tons in 1730 to 75 tons in 1773. The product was shipped in over two thousand chests, each containing 140 pounds (64 kg) of opium.[21]
and
British military superiority drew on newly applied technology. British warships wreaked havoc on coastal towns; the steam ship Nemesis was able to move against the winds and tides and support a gun platform with very heavy guns. In addition, the British troops were the first to be armed with modern muskets and cannons, which fired more rapidly and with greater accuracy than the Qing firearms and artillery, though Chinese cannons had been in use since previous dynasties. After the British took Canton, they sailed up the Yangtze and took the tax barges, a devastating blow to the Empire as it slashed the revenue of the imperial court in Beijing to just a fraction of what it had been.
and
Click to access RL34314.pdf
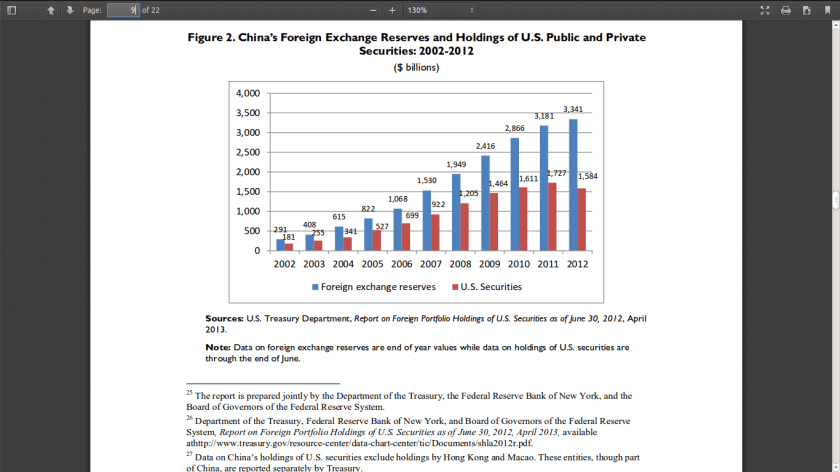
China’s Holdings of U.S. Securities: Implications for the U.S. Economy
Notice how Chinese purchases of US Treasury mirror the rise in Opium purchases.
A technical default by US due to internal politics can enhance conflict and stress between China
It offers a great opportunity for the US to virtually cancel the US debt into half, by going into conflict.
The window of opportunity for US military superiority over China is limited- within a decade China would no longer be a generation behind US Aircraft Carriers.
—
So the US might just make a huge profit because of the shutdown. Still think that Boehner is crazy?
ps- In 1858, about twenty years after the first Opium War, the annual import rose to 70,000 chests (4,480 tons), approximately equivalent to global production of opium for the decade surrounding the year 2000
28.635308
77.224960
















 The recommended keywords is designed very nicely and subtly. You can click on screenshots for a better look (links have been updated)
The recommended keywords is designed very nicely and subtly. You can click on screenshots for a better look (links have been updated) NumPy is the fundamental package needed for scientific computing with Python. Besides its obvious scientific uses, NumPy can also be used as an efficient multi-dimensional container of generic data. Arbitrary data-types can be defined. This allows NumPy to seamlessly and speedily integrate with a wide variety of databases. Repositories for NumPy binaries:
NumPy is the fundamental package needed for scientific computing with Python. Besides its obvious scientific uses, NumPy can also be used as an efficient multi-dimensional container of generic data. Arbitrary data-types can be defined. This allows NumPy to seamlessly and speedily integrate with a wide variety of databases. Repositories for NumPy binaries:  SciPy is open-source software for mathematics, science, and engineering. It is also the name of a very popular conference on scientific programming with Python. The SciPy library depends on NumPy, which provides convenient and fast N-dimensional array manipulation. The SciPy library is built to work with NumPy arrays, and provides many user-friendly and efficient numerical routines such as routines for numerical integration and optimization.
SciPy is open-source software for mathematics, science, and engineering. It is also the name of a very popular conference on scientific programming with Python. The SciPy library depends on NumPy, which provides convenient and fast N-dimensional array manipulation. The SciPy library is built to work with NumPy arrays, and provides many user-friendly and efficient numerical routines such as routines for numerical integration and optimization. 2D plotting library for Python that produces high quality figures that can be used in various hardcopy and interactive environments. matplolib is compatiable with python scripts and the python and ipython shells.
2D plotting library for Python that produces high quality figures that can be used in various hardcopy and interactive environments. matplolib is compatiable with python scripts and the python and ipython shells. High quality open source python shell that includes tools for high level and interactive parallel computing.
High quality open source python shell that includes tools for high level and interactive parallel computing. SymPy is a Python library for symbolic mathematics. It aims to become a full-featured computer algebra system (CAS) while keeping the code as simple as possible in order to be comprehensible and easily extensible. SymPy is written entirely in Python and does not require any external libraries.
SymPy is a Python library for symbolic mathematics. It aims to become a full-featured computer algebra system (CAS) while keeping the code as simple as possible in order to be comprehensible and easily extensible. SymPy is written entirely in Python and does not require any external libraries. Cython is a language based on Pyrex that makes writing C extensions for Python as easy as writing them in Python itself. Cython supports calling C functions and declaring C types on variables and class attributes, allowing the compiler to generate very efficient C code from Cython code.
Cython is a language based on Pyrex that makes writing C extensions for Python as easy as writing them in Python itself. Cython supports calling C functions and declaring C types on variables and class attributes, allowing the compiler to generate very efficient C code from Cython code. pandas is an open source, BSD-licensed library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language.
pandas is an open source, BSD-licensed library providing high-performance, easy-to-use data structures and data analysis tools for the Python programming language. PyTables is a package for managing hierarchical datasets and designed to efficiently and easily cope with extremely large amounts of data. PyTables is built on top of the HDF5 library, using the Python language and the NumPy package. It features an Pythonic interface combined with C / Cython extensions for the performance-critical parts of the code. This makes it a fast, yet extremely easy to use tool for very large amounts of data.
PyTables is a package for managing hierarchical datasets and designed to efficiently and easily cope with extremely large amounts of data. PyTables is built on top of the HDF5 library, using the Python language and the NumPy package. It features an Pythonic interface combined with C / Cython extensions for the performance-critical parts of the code. This makes it a fast, yet extremely easy to use tool for very large amounts of data.  Free high-quality and peer-reviewed volunteer produced collection of algorithms for image processing.
Free high-quality and peer-reviewed volunteer produced collection of algorithms for image processing. Module designed for scientific pythons that provides accesible solutions to machine learning problems.
Module designed for scientific pythons that provides accesible solutions to machine learning problems. Statsmodels is a Python package that provides a complement to scipy for statistical computations including descriptive statistics and estimation of statistical models.
Statsmodels is a Python package that provides a complement to scipy for statistical computations including descriptive statistics and estimation of statistical models. Interactive development environment for Python that features advanced editing, interactive testing, debugging and introspection capabilities, as well as a numerical computing environment made possible through the support of Ipython, NumPy, SciPy, and matplotlib.
Interactive development environment for Python that features advanced editing, interactive testing, debugging and introspection capabilities, as well as a numerical computing environment made possible through the support of Ipython, NumPy, SciPy, and matplotlib. Theano is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently.
Theano is a Python library that allows you to define, optimize, and evaluate mathematical expressions involving multi-dimensional arrays efficiently. Open source mathematics sofware system that combines existing open-source packages into a Python-based interface.
Open source mathematics sofware system that combines existing open-source packages into a Python-based interface. Free scientific and engineering development software used for numerical computations, and analysis and visualization of data using the Python programmimg language.
Free scientific and engineering development software used for numerical computations, and analysis and visualization of data using the Python programmimg language.