A software called saspy helps SAS and Python work together
https://blogs.sas.com/content/sasdummy/2017/04/08/python-to-sas-saspy/
Python coders can now bring the power of SAS into their Python scripts. The project is SASPy, and it’s available on the SAS Software GitHub. It works with SAS 9.4 and higher, and requires Python 3.x.
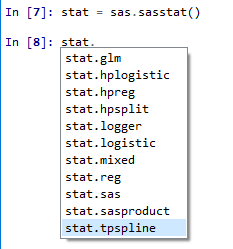

and its available at Github
https://github.com/sassoftware/saspy
A Python interface to MVA SAS
This module allows a python process to connect to SAS 9.4 and run SAS code, generated by the supplied object and methods or explicitly user written, and returns results as text, HTML5 documents (via SAS ODS), or as Pandas Data Frames. It supports running analytics and returning the resulting graphics and result data. It can convert between SAS Data Sets and Pandas Data Frames. It has multiple access methods which allow it to connect to local or remote Linux SAS, IOM SAS on Windows or Linux (Including Grid Manager), and local PC SAS. It can run w/in Jupyter Notebooks, in line mode python or in python batch scripts. It is expected that the user community can and will contribute enhancements.
Clearly SAS has made tremendous progress in reaching out to the open source community from releasing the free SAS University Edition to latest products like SAS Viya (https://www.sas.com/en_in/software/viya.html )
With SAS Viya, it’s now possible to integrate all elements needed to
build and deploy analytics – whether they are defined in SAS, written
with other programming languages like Python, Java, R or Lua, or
called from public REST APIs.https://www.sas.com/content/dam/SAS/en_us/doc/overviewbrochure/sas-viya-108233.pdf
But is too little too late for SAS or is it the other way around for R, with Python usage increasing rapidly and R’s much vaunted libraries ported with ease, much better documentation and enterprise customer support in SAS and Python than in R.
As they say, time will tell? Meanwhile the data science and big data market is booming and there seems enough for all to share slices of market share


 IP address for connecting 192.168.72.128
IP address for connecting 192.168.72.128